PCB Assembly Methods: Through-Hole vs. Surface-Mount Technology (SMT)
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are foundational to modern electronics, but how components are mounted onto these boards can vary depending on design, application, and performance needs. Two primary PCB assembly methods dominate the electronics manufacturing: Through-Hole Technology (THT) and Surface-Mount Technology (SMT). Each offers unique benefits and considerations. In this article, we’ll break down the differences between these two approaches and help you understand which is right for your product.
What Is Through-Hole Technology (THT)?
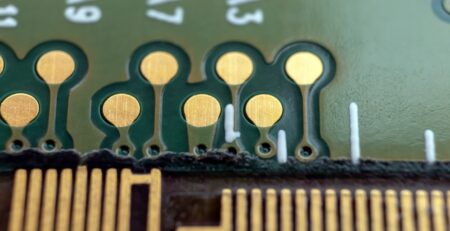
Through-hole technology involves inserting the leads of electronic components through pre-drilled holes in the PCB. The component leads are then soldered to pads on the opposite side of the board, creating a strong mechanical bond.
Advantages of THT:
- Superior mechanical strength for components under physical stress
- Ideal for larger components like connectors, capacitors, and transformers
- Better suited for high-reliability applications such as military and aerospace
Limitations of THT:
- Requires drilling, which adds to manufacturing cost and time
- Limits board layout flexibility and component density
What Is Surface-Mount Technology (SMT)?
Surface-mount technology allows components to be mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB without the need for holes. These components, known as surface-mount devices (SMDs), are soldered to pads on the board’s surface, enabling high-speed automated assembly and compact design.
Advantages of SMT:
- Smaller component size enables higher component density
- Faster, more cost-effective automated assembly
- Ideal for lightweight and compact devices
- Supports both sides of the PCB for assembly
Limitations of SMT:
- Not as mechanically robust as THT for high-stress environments
- More sensitive to thermal and mechanical stress during handling
How to Choose Between THT and SMT
Selecting the right PCB assembly method depends on your product’s design, environment, and application. Here are some factors to consider:
- Will the product experience mechanical stress or vibration?
- Is miniaturization a top priority?
- What is the volume and cost sensitivity of production?
- Are there regulatory or durability requirements to meet?
In many cases, a hybrid approach is used—employing SMT for the majority of components and THT for connectors or large parts.
SVTronics Supports Both THT and SMT Assembly
At SVTronics, we offer full-service PCB assembly capabilities, including both through-hole and surface-mount technologies. Whether your design demands rugged durability, high-speed processing, or miniaturization, our experienced team and advanced equipment ensure precision and performance at every step.
Contact SVTronics for PCB Assembly Guidance
Understanding the differences between THT and SMT is essential for making the right choice in your PCB assembly design and manufacturing strategy. If you’re unsure which method best fits your product, SVTronics is here to help with expert guidance, advanced engineering, and end-to-end electronic manufacturing solutions.











Leave a Reply